Table of Contents
The MPFQ library is currently developped mostly for the
x86_64 architecture (Intel's Core2 and AMD's Opteron
processors). In principle, there is a plain C fallback implementation
based on GMP for each function; so any hardware supported by GMP
should be ok.
As for the operating system, the library is developped under GNU-Linux; it is expected to be not too hard to port to other Unices, but this is not thoroughly tested.
MPFQ requires some tools for the automatic code generation, and for the compilation:
Perl. Tested with versions 5.8.8 and higher
GCC. Better choose a version 4.x or higher. Beware. GCC versions 4.3.0 and 4.3.1 suffer from a severe bug (numbered 37101 in GCC's bug tracking system) which affects SSE-2 code generation. This may impact generated code for
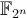 unpredictably, the outcome
being wrong generated code. For
this reason, these compiler versions should be avoided. The
bug in question is fixed in GCC 4.3.2.
unpredictably, the outcome
being wrong generated code. For
this reason, these compiler versions should be avoided. The
bug in question is fixed in GCC 4.3.2.
GMP. Tested with version 4.2.2 and higher. Must be compiled without nails. If you give the location of
gmp-impl.handlonglong.h, this might yield a speed up to MPFQ.CMake. Last tested with 2.8.9 ; should work with most recent versions as well.
Building the documentation (which you are currently reading, so probably of little interest) requires some additional tools:
A complete tool chain for generating docbook documents. This includes in particular the
xmllintandxsltprocprograms, as well as the standard DocBook DTDs and style sheets. The corresponding packages are available in most Linux distributions.Tools for parsing latex-style math text, and converting this to png images. The current scripts included with MPFQ achieve this goal using the following programs:
latex
ImageMagick